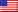
Blue Origin is preparing to demonstrate the reusability of its New Glenn rocket by reflying a previously used booster on its upcoming mission, targeted for late February. This flight, designated NG-3, will carry a massive Block 2 BlueBird satellite for AST SpaceMobile, a company building a direct-to-cellphone internet constellation.
New Glenn’s Reusability Milestone
This mission marks a significant step for New Glenn, one of the world’s largest rockets at 322 feet tall. The first stage booster will be the same one used on the NG-2 flight in November, which successfully delivered NASA’s ESCAPADE Mars probes to orbit. Blue Origin designed New Glenn for extensive reuse – aiming for at least 25 flights per booster. The company has already proven the concept with New Shepard, its suborbital rocket, which has flown 38 times, including 17 crewed missions.
The Block 2 BlueBird Satellite
The payload, AST SpaceMobile’s Block 2 BlueBird, is a particularly large satellite, with antennas spanning 2,400 square feet. These massive satellites are designed to beam internet connectivity directly to mobile phones, bypassing the need for traditional cell towers in remote areas. AST SpaceMobile has already launched smaller first-generation BlueBirds, but the Block 2 version represents a substantial increase in capacity.
Implications for Space Launch Costs
Blue Origin’s decision to reuse a booster reflects a broader trend in the space industry towards cost reduction through reusability. SpaceX has pioneered this approach with its Falcon 9 rockets, and now Blue Origin is following suit with New Glenn. By reusing hardware, launch providers can significantly lower the price per flight, making space access more affordable for both commercial and government customers.
The NG-3 mission will launch from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, continuing the pattern established by New Glenn’s first two flights. If successful, this reflight will further validate Blue Origin’s reusability strategy and position New Glenn as a competitive option in the heavy-lift launch market.